Artificial Intelligence (AI) is fundamentally reshaping industries, global markets, and economic landscapes. As businesses and governments recognize the transformative power of AI, its impact is poised to accelerate across sectors, driving unprecedented growth and productivity. According to a PwC report, AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, accounting for a 14% boost in global GDP. This projection stems from the rapid adoption of AI technologies across various industries, including retail, finance, and healthcare, which are leading the way in embracing AI to enhance productivity, product quality, and consumption.
In retail, AI-powered solutions streamline operations, optimize supply chains, and enable personalized consumer experiences. Similarly, in finance, AI is revolutionizing risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service through intelligent automation. The healthcare sector benefits from AI's ability to enhance diagnostics, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. The integration of AI across these key sectors not only drives operational efficiency but also creates new market opportunities that could spur economic growth for years to come.
As businesses prepare for this AI-driven future, the potential for economic transformation is significant. With estimates suggesting that China and North America could experience GDP boosts of 26% and 14%, respectively, by 2030, the global shift towards AI adoption is set to reshape economies and industries at an unprecedented scale.
The era of AI transformation is upon us, offering businesses a once-in-a-generation opportunity to harness its economic potential. As AI technologies continue to evolve, the sectors that act now stand to reap the most significant rewards in terms of productivity, market share, and innovation. Responsible adoption and strategic investment in AI will be key to ensuring long-term growth and competitiveness in this rapidly changing economic landscape.
The Global Economic Potential of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize the global economy, with projections indicating a 14% boost in global GDP by 2030. This translates into an economic contribution of up to $15.7 trillion. The adoption of AI technologies is expected to drive this growth through two primary mechanisms: productivity gains and increased consumption. By automating routine tasks, enhancing decision-making, and personalizing products and services, AI empowers businesses to operate more efficiently while offering consumers improved experiences.
Emerging markets like China and North America are expected to see significant economic growth from AI. China is projected to experience a staggering 26% increase in GDP by 2030, while North America is anticipated to see a 14% rise. These regions are at the forefront of AI adoption, driven by substantial investments in AI research, development, and infrastructure. For example, the global AI market size is expected to surge from $214.6 billion in 2024 to over $1.3 trillion by 2030, fueled by advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and generative AI.
Productivity gains will play a crucial role in AI’s economic impact. AI has the potential to automate up to 25% of tasks in advanced economies and 10-20% in emerging markets. This automation frees up labor for higher-value activities, improving efficiency across industries. In sectors like healthcare, finance, and retail, AI-driven innovations are already enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling more personalized services. For example, in healthcare, AI is revolutionizing diagnostics and treatment personalization.
Consumption is another key driver of AI's economic influence. The increasing availability of AI-enhanced products and services is expected to stimulate consumer demand, contributing to over 55% of the GDP gains associated with AI by 2030. As AI technologies become more widespread, businesses will be able to offer highly customized and higher-quality products, further fueling economic growth.
AI’s potential to transform the global economy is vast. With the right investments and strategic adoption, businesses can capitalize on this technological revolution, driving productivity and fostering long-term economic growth across the globe. The significant gains expected in regions like China and North America exemplify the opportunities AI presents for economies worldwide.
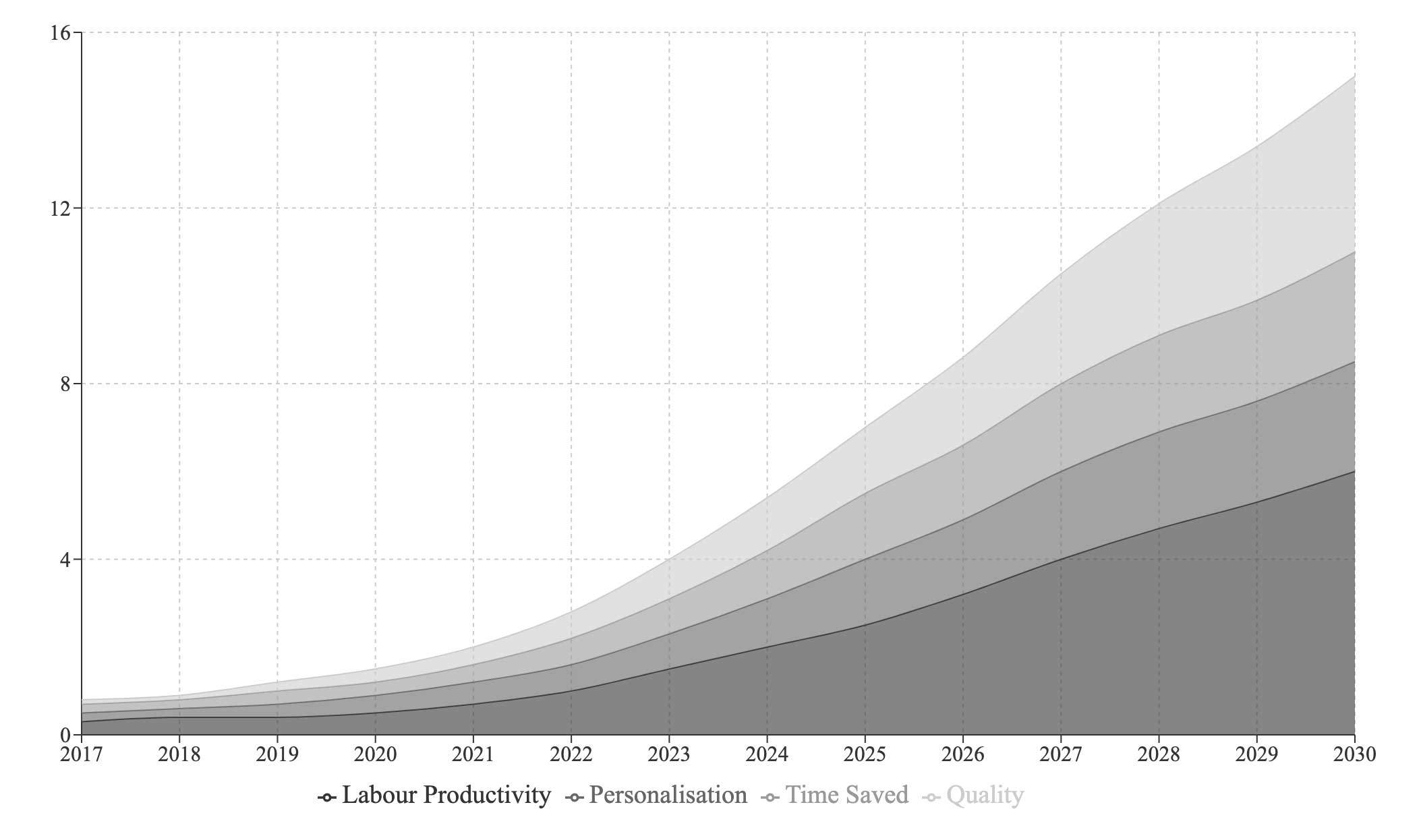
AI’s Role in Productivity and Business Efficiency
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how businesses operate by automating both manual and cognitive tasks, leading to significant boosts in productivity and efficiency across various industries. In particular, sectors such as financial services, manufacturing, and logistics are witnessing a revolutionary shift driven by AI technologies.
Automating Manual and Cognitive Tasks
AI has demonstrated its ability to enhance business efficiency by automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. In the manufacturing sector, AI-powered robots and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into production lines to perform tasks such as assembly, quality control, and predictive maintenance. These technologies allow businesses to operate with greater precision, speed, and reduced costs.
For instance, in Industry 4.0 settings, AI is used to optimize supply chains, enhance production processes, and predict equipment failures before they occur. Companies like ZEISS are at the forefront of this transformation, utilizing AI to monitor manufacturing processes, detect defects in real-time, and adjust operations autonomously to improve product quality and reduce waste. Predictive maintenance powered by AI helps reduce unplanned downtimes and extends the life of machinery, which leads to significant cost savings.
Similarly, in logistics, AI algorithms streamline routing and inventory management, reducing delivery times and operational inefficiencies. By leveraging AI, companies can forecast demand more accurately, optimize warehousing, and manage fleets more efficiently, resulting in faster delivery and cost reduction.
AI in Financial Services
The financial services sector has also embraced AI, particularly in automating cognitive tasks such as risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service. AI systems can process vast amounts of financial data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies faster than any human analyst. This allows financial institutions to not only prevent fraudulent activities but also provide personalized services to their customers. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have become common in customer service, offering quick and accurate responses to client inquiries, further improving operational efficiency.
For example, JPMorgan Chase has deployed AI to streamline processes in asset management, where AI-driven models help portfolio managers make better investment decisions. AI systems can analyze market trends and forecast potential risks, allowing financial firms to respond swiftly to market changes.
Case Studies in Manufacturing and Logistics
In manufacturing, AI is driving the development of "smart factories," where machines communicate with one another to make real-time adjustments during production. Companies like ZEISS are integrating machine learning into their manufacturing lines to identify defects and optimize processes autonomously. This not only increases production efficiency but also improves product quality while reducing material waste.
The logistics sector is similarly benefiting from AI advancements. AI enables companies to predict maintenance needs for delivery vehicles, optimize routes to reduce fuel consumption, and manage supply chains more effectively. For instance, edge AI solutions allow data processing to be conducted closer to the source, reducing latency and improving decision-making in logistics operations.
AI's role in enhancing productivity and business efficiency is undeniable, particularly in industries such as financial services, manufacturing, and logistics. By automating manual and cognitive tasks, AI reduces operational costs, increases speed, and improves overall output. As businesses continue to integrate AI into their operations, the potential for innovation and efficiency gains will only grow. Moving forward, the challenge will be ensuring the interoperability of AI systems to maximize their impact across all sectors.
Generative AI and Emerging Technologies
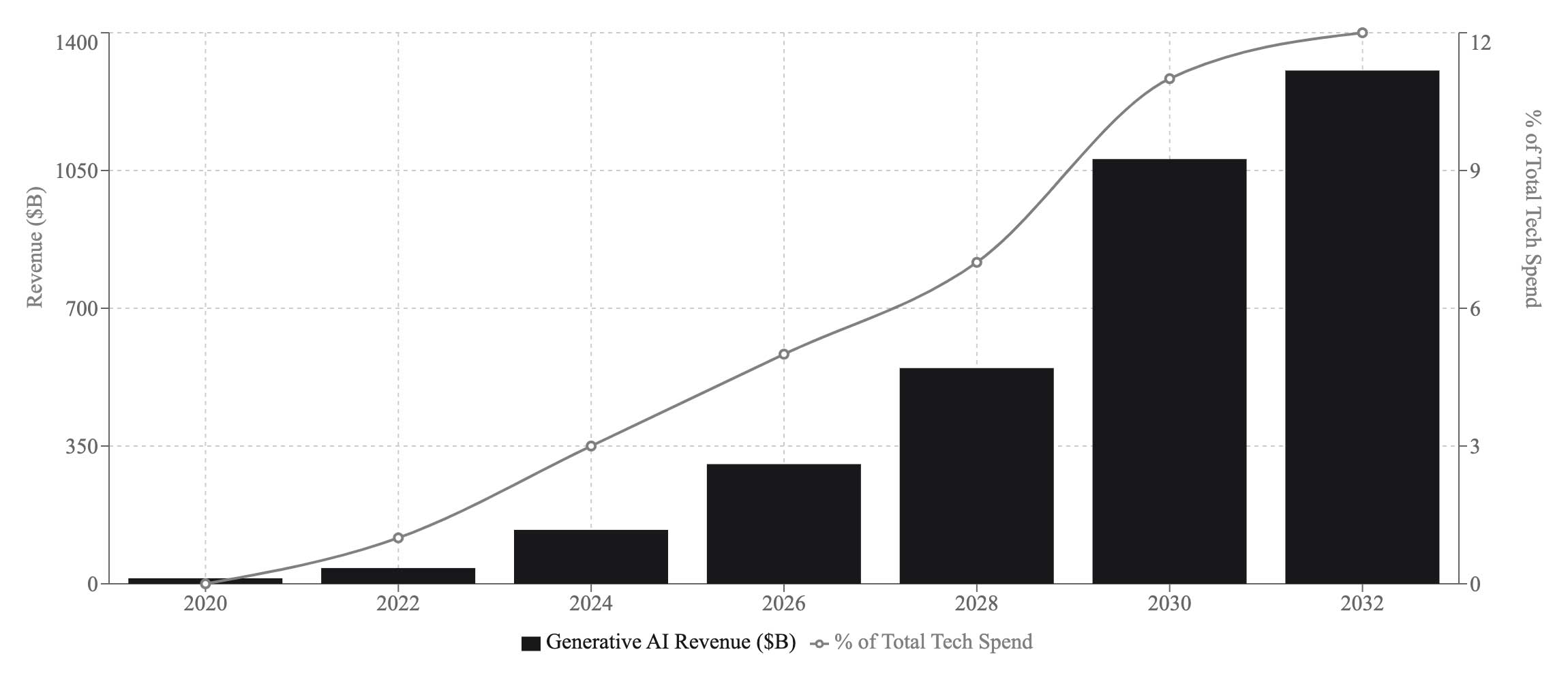
Generative AI is emerging as a game-changing technology, with forecasts suggesting it could become a $1.3 trillion market by 2032. This new wave of AI is reshaping industries by driving innovations across sectors such as natural language processing (NLP), image creation, design, and customer service. Its ability to produce new content autonomously and its growing application in business processes make it one of the most significant technological trends of the coming decade.
Generative AI's Projected Growth and Economic Impact
Generative AI holds the potential to radically transform global economic landscapes. Goldman Sachs predicts that generative AI could start significantly contributing to US GDP by 2027. This shift is fueled by the ability of generative AI to automate complex cognitive tasks, which were traditionally labor-intensive, such as drafting reports, designing visuals, or even composing music. Businesses across industries are already making strategic investments in generative AI to enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and unlock new revenue streams.
While the adoption of generative AI is still in its early stages, its applications are expanding rapidly. From automating content creation to enabling advanced design processes, generative AI is enhancing both efficiency and creativity. AI's capability to mimic human-like outputs is paving the way for greater innovation, particularly in sectors like entertainment, where AI-generated content is gaining traction.
Innovation in Natural Language Processing and Image Creation
One of the most transformative applications of generative AI is in natural language processing (NLP) and image generation. With advancements in AI models like GPT and DALL·E, machines are now capable of producing human-like text and generating visually compelling images autonomously. These capabilities are revolutionizing industries such as marketing, where AI-generated content can be tailored to specific audiences at unprecedented speeds.
In customer service, NLP-powered AI systems are transforming how businesses handle customer interactions. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can resolve complex inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and improve overall customer engagement. By automating responses and generating real-time insights, AI is not only improving customer service but also freeing up human agents to handle more intricate tasks.
Applications of Generative AI in Design, Content Creation, and Customer Support
Generative AI is making significant strides in creative industries, particularly in design and content production. In design, AI-driven generative models can create countless variations of products based on specific constraints like cost, materials, and performance requirements. This accelerates the design process, allowing engineers and designers to explore a broader range of possibilities while saving time and resources.
In content creation, AI is being used to automate the production of articles, social media posts, and marketing copy. AI-generated content is highly customizable and can be produced at scale, enabling businesses to meet the increasing demand for personalized and timely content without overburdening human creators. For instance, companies are using AI to produce dynamic content that adapts to user preferences, increasing engagement and driving better marketing results.
In the realm of customer service, generative AI is revolutionizing how businesses interact with their clients. AI can now generate personalized responses to customer inquiries, analyze historical data to predict future needs, and provide automated recommendations for customer support agents. These tools help businesses enhance their service offerings while significantly reducing operational costs.
Generative AI represents a major leap forward in both technological capability and economic potential. Its growth into a $1.3 trillion market by 2032 highlights the immense value that businesses can capture by integrating AI into their operations. From content creation and design to customer service, the transformative power of generative AI is set to redefine industries, offering businesses new ways to innovate, compete, and thrive in an increasingly automated world. As the adoption of generative AI accelerates, early movers will gain a competitive edge, positioning themselves to lead in this next phase of the digital economy.
AI in Decision-Making and Business Strategy
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming decision-making processes within businesses, offering advanced tools to augment human judgment. By processing vast amounts of data with unprecedented speed and accuracy, AI enables companies to make more informed, data-driven decisions. This shift towards AI-powered decision-making is fundamentally changing business strategy across industries, enhancing efficiency, reducing risks, and allowing for more personalized interactions with customers.
Augmenting Decision-Making Through Advanced Analytics
AI enhances decision-making by providing deep insights through advanced analytics. These systems can analyze large datasets, identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that might otherwise go unnoticed. This allows executives and managers to base their strategic decisions on accurate, real-time data rather than intuition or guesswork. Predictive analytics, in particular, empowers companies to forecast trends, manage risks, and make proactive decisions that can optimize operations and drive growth.
In industries like healthcare, AI-driven analytics are being used to predict patient outcomes and optimize treatment plans, significantly improving the quality of care. These systems analyze vast amounts of data, from patient records to medical imaging, to support clinicians in making faster, more accurate diagnoses. In marketing, AI's ability to analyze customer behavior helps companies tailor their campaigns to specific audience segments, improving engagement and return on investment.
Real-World Examples of AI-Driven Decision-Making
One of the most profound impacts of AI on business strategy is its ability to improve decision-making in sectors such as healthcare and marketing. In healthcare, AI-powered diagnostic tools are transforming how diseases are detected and treated. For example, AI systems can now analyze medical images to identify early signs of diseases like cancer, helping doctors catch potential issues sooner and with greater accuracy. AI is also used to optimize hospital operations, predict patient admissions, and improve resource allocation.
In the retail and marketing sectors, AI-driven decision-making is revolutionizing customer engagement strategies. Retailers use AI to analyze purchasing patterns, optimize inventory management, and predict product demand. This ensures that they can meet customer needs more effectively while minimizing waste and overproduction. AI also enables real-time adjustments to marketing strategies, allowing companies to personalize their messages and offers based on customer behavior, which enhances engagement and drives sales.
Impact on Personalized Consumer Experiences
AI has revolutionized personalized consumer experiences by enabling businesses to offer tailored services and products at scale. By analyzing customer data, including past purchases, browsing history, and preferences, AI can deliver highly customized recommendations, making interactions more relevant and satisfying for consumers. E-commerce platforms, for instance, leverage AI to suggest products that align with individual user preferences, driving higher conversion rates and improving customer loyalty.
Additionally, AI-powered customer service tools, such as chatbots, provide instant, personalized responses to inquiries. These systems can learn from previous interactions, continuously improving their ability to address customer needs more effectively. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also allows businesses to operate more efficiently by reducing the burden on human customer service agents.
AI is playing an increasingly central role in shaping business strategy and decision-making across industries. By leveraging advanced analytics, predictive models, and real-time data processing, AI allows businesses to make more informed, accurate decisions. Furthermore, its ability to deliver personalized consumer experiences is reshaping how companies interact with their customers, fostering deeper connections and driving better business outcomes. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on decision-making and strategy will only become more pronounced, offering businesses powerful tools to navigate the complexities of the modern market.
AI’s Impact on Labor Markets and Employment
As AI continues to reshape industries, its impact on labor markets is both profound and multifaceted. The key concerns revolve around AI's potential to displace jobs, while simultaneously creating new opportunities, particularly in highly skilled industries. This dual effect underscores the need for a nuanced approach to understanding AI's role in transforming labor dynamics and addressing economic inequality.
AI-Induced Job Displacement vs. Job Creation
One of the most widely debated consequences of AI is the displacement of jobs. Automation and AI technologies are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from routine administrative work to more complex functions such as data analysis and even medical diagnostics. Estimates suggest that by 2030, as many as 400 million to 800 million jobs globally could be displaced by AI and automation, forcing millions of workers to switch industries and acquire new skills.
However, this displacement is expected to be counterbalanced by the creation of new jobs, particularly in sectors that AI cannot fully automate. These new roles will likely be concentrated in fields requiring advanced technical skills, such as IT, engineering, and healthcare. AI will also fuel growth in creative industries, as rising incomes drive demand for leisure and entertainment, further expanding employment opportunities.
In highly skilled industries, AI is not merely replacing jobs but is augmenting human labor. For example, in healthcare, AI-powered tools are assisting doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately and efficiently, allowing them to focus on more complex cases that require human expertise. Similarly, in finance, AI enhances the work of analysts by processing large datasets, identifying trends, and offering actionable insights, enabling professionals to make better-informed decisions faster.
Augmenting Human Work in Highly Skilled Industries
While concerns about job displacement are legitimate, AI is also increasingly being used to complement and enhance human labor, particularly in knowledge-based industries. In fields such as healthcare, finance, and education, AI is augmenting the capabilities of professionals rather than replacing them. This shift, often referred to as "augmented intelligence," allows workers to focus on tasks that require creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making, while AI handles more routine and data-driven processes.
For example, in healthcare, AI systems are used to process medical data, predict patient outcomes, and assist in surgery, helping healthcare professionals deliver better care with greater efficiency. In education, AI is being used to personalize learning experiences, allowing educators to tailor their teaching methods to the needs of individual students. These applications demonstrate how AI can enhance productivity while improving the quality of work in high-skill sectors.
The Transformation of Labor Dynamics and Economic Inequality
AI's influence on labor markets is also contributing to changes in labor dynamics and economic inequality. Workers who are able to adapt to AI and acquire the necessary skills will likely see an increase in their productivity and wages. Conversely, those who cannot make the transition may find themselves left behind, exacerbating income inequality.
The introduction of AI into the workforce is also reshaping how labor is organized. The rise of gig and freelance work, facilitated by AI-powered platforms, is creating new opportunities for flexible employment but also raising concerns about job security and benefits. Additionally, AI-driven automation is likely to affect low-income workers more severely than their higher-income counterparts, as the tasks typically performed by low-wage workers are more susceptible to automation.
Addressing these challenges will require concerted efforts by policymakers, businesses, and educational institutions. Investments in retraining programs, lifelong learning opportunities, and social safety nets will be crucial to ensuring that workers can transition into new roles created by AI. Without such measures, AI could deepen existing inequalities within and between countries, with advanced economies reaping the majority of AI's benefits while emerging markets struggle to keep pace.
AI is set to transform labor markets globally, bringing both opportunities and challenges. While it is likely to displace millions of jobs, it will also create new roles and enhance the capabilities of workers, particularly in highly skilled industries. However, the uneven distribution of AI's benefits could exacerbate economic inequality, making it imperative for governments and businesses to implement policies that promote inclusive growth. As AI continues to evolve, the focus must shift from fearing job displacement to embracing the potential for AI to enhance human work and foster a more productive and equitable labor market.
AI's Future in Global Business Strategy
As we look toward the future, AI's role in global business strategy is poised to be transformative across industries, economies, and cultures. AI is not merely a trend but a driving force for innovation, unlocking new possibilities in business efficiency, product development, and consumer experiences.
The future of AI adoption will involve a delicate balance between automation, augmentation, and human decision-making. While AI promises to revolutionize areas like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, businesses must focus on responsible AI adoption. This includes building transparent AI systems that maintain trust with consumers and stakeholders, ensuring governance and mitigating risks related to privacy, security, and ethical use.
To capitalize on AI's potential, businesses must actively invest in AI technology and infrastructure. Those who move quickly to integrate AI into their operations will gain a significant competitive edge. AI frontrunners are likely to lead in customer insight, personalization, and efficiency, but success will require comprehensive strategies to leverage AI responsibly and sustainably.
As industries evolve, AI will enhance labor productivity, drive economic growth, and catalyze new business models. The challenge for businesses lies not only in adopting AI but also in developing the talent, culture, and governance frameworks necessary to sustain this innovation. Companies that invest in AI today are positioning themselves for long-term success and competitiveness in a rapidly changing global economy.
references
- PwC | Artificial Intelligence Study
- Markets and Markets | Artificial Intelligence Market Report
- Goldman Sachs | AI is Showing Very Positive Signs of Boosting GDP
- Goldman Sachs | AI May Start to Boost US GDP in 2027
- World Scientific | Industry 4.0
- ZEISS | AI in Industry 4.0
- JPMorgan | How AI Can Boost Productivity and Jump-Start Growth
- Bloomberg | Generative AI to Become a $1.3 Trillion Market by 2032
- McKinsey | Jobs Lost, Jobs Gained: What the Future of Work Will Mean for Jobs, Skills, and Wages
Please Note: This content was created with AI assistance. While we strive for accuracy, the information provided may not always be current or complete. We periodically update our articles, but recent developments may not be reflected immediately. This material is intended for general informational purposes and should not be considered as professional advice. We do not assume liability for any inaccuracies or omissions. For critical matters, please consult authoritative sources or relevant experts. We appreciate your understanding.
