The year 2024 marks a pivotal moment in the global technological landscape, especially for the AI sector. AI has not only established itself as the leading frontier of innovation but is also reshaping industries at an unprecedented pace. From healthcare to marketing, financial services to autonomous systems, the applications of AI are vast and expanding rapidly. The Bain 2024 Technology Report highlights that AI’s adoption rates across sectors have soared, with enterprises significantly increasing their investments to harness its transformative potential. However, there are growing concerns regarding return on investment, with skeptics emphasizing that AI’s value doesn’t lie solely in its deployment. Instead, real value emerges from integrating AI into business operations, restructuring workflows, and managing organizational changes to support its effectiveness.
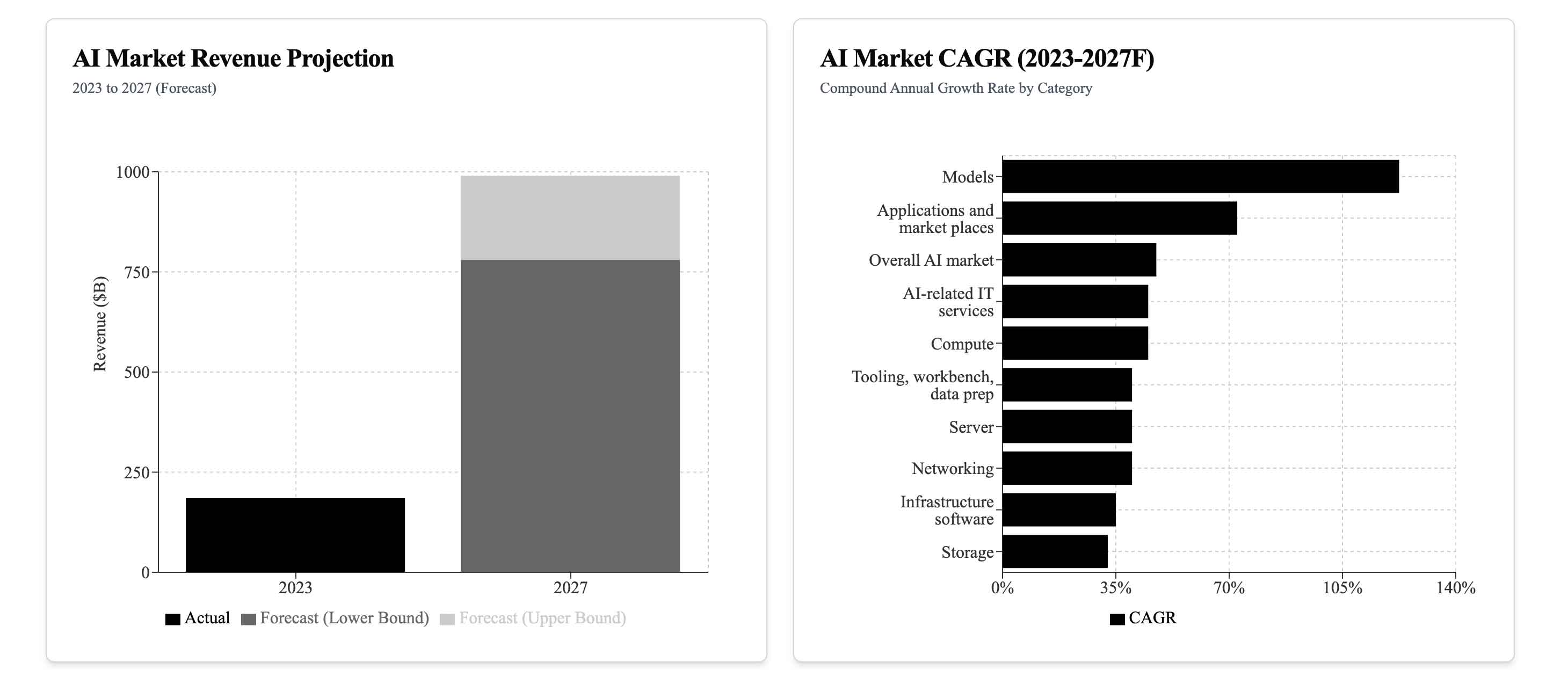
This current AI boom differs from previous technological waves, such as the internet or mobile revolutions. For the first time, large tech incumbents like Microsoft, Nvidia, and Amazon are leading the charge, funding capital-heavy startups like OpenAI, Anthropic, and CoreWeave. This shift, as explored in various reports, indicates that traditional venture capital firms are no longer at the center of the innovation ecosystem. Tech giants are leveraging their immense financial resources and strategic advantages—cloud infrastructure, business partnerships, and more—to drive forward AI development.
What makes 2024 so unique is the convergence of multiple factors: the economic pressure to innovate, the staggering influx of investment capital, and the growing competition among tech leaders to remain relevant. Goldman Sachs' analysis underscores that, unlike previous bubbles, AI investments today are grounded in strong financial fundamentals and massive market potential. Yet, with so much capital concentrated in the hands of a few dominant players, there are real risks of market concentration and monopolization.
For tech companies, both startups and established enterprises, navigating this new AI-driven landscape requires a strategic roadmap. This article will offer that roadmap—dissecting the opportunities and challenges of the AI era, while providing actionable insights for tech leaders aiming to not only survive but thrive during this transformative period.
To serve as a comprehensive guide, this article will examine the key shifts in the AI market, explore strategies for sustainable growth, and delve into the operational and financial imperatives that are driving the current AI boom. Tech companies will need to stay agile, innovative, and adaptive to continue leading in this AI-first world.
AI’s Disruption: A Tech Renaissance
In 2024, artificial intelligence is driving one of the most profound technological transformations in history. The explosive growth across sectors fueled by AI is reshaping industries, creating new opportunities while also presenting significant challenges. From healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing, AI's capabilities are advancing at breakneck speed, integrating into critical business functions such as supply chain optimization, customer experience, and predictive analytics
Big Tech’s Role in Reshaping Industries
The key difference in this AI era, compared to past technological booms, lies in the central role of Big Tech. Unlike previous innovations driven by venture capital (VC), the current wave of AI is being heavily funded by tech giants like Microsoft, Amazon, Nvidia, and Alphabet. These companies, with their vast financial resources, are not just funding AI development—they are leading it. For instance, Nvidia has become a dominant player in AI infrastructure, with its GPUs being essential for training large AI models, and Microsoft has integrated AI tools like OpenAI’s GPT into its cloud services.
The financial muscle and computational infrastructure of these companies give them an edge over traditional VC-backed startups. As Bain & Company reports, these tech giants are leveraging their scale to dominate AI, not only in innovation but also in business ecosystems. This “winner takes most” dynamic is creating significant barriers to entry for new players.
However, Big Tech’s dominance is not unchallenged. While they control much of the AI infrastructure, smaller startups and disruptors are focusing on niche applications and services that require less capital. These companies, while constrained in their resource allocation, are developing specialized AI solutions that challenge the incumbents by offering tailored and agile responses to market needs.
The New Rules of Competition in the AI Era
In this new competitive landscape, success is no longer defined by rapid growth alone but by the ability to innovate at scale and capture value from AI investments. As MIT Technology Review notes, many enterprises underestimate the technical and operational challenges associated with deploying AI. Companies that effectively integrate AI not only optimize existing operations but also disrupt entire business models.
Generative AI, in particular, is creating new paradigms in product development, marketing, and customer engagement. This shift is forcing companies to rethink how they operate, with the focus shifting from broad technological adoption to strategic, data-driven applications that enhance efficiency and personalize customer experiences.
In this AI era, competition revolves around who can best leverage AI to unlock hidden value in data, streamline operations, and create innovative customer solutions. The companies that successfully do so are positioning themselves as leaders in the next phase of the digital economy.
Financial Shifts: The Changing Landscape of Tech Profitability
In 2024, tech companies are experiencing significant shifts in profitability, largely driven by the explosion of AI. While profits are rising for many leading players, the landscape is increasingly characterized by high costs and capital-intensive models, particularly in AI infrastructure. For instance, AI startups are achieving revenue milestones faster than previous generations of tech companies, yet they face intense pressure from the high costs of cloud computing and AI model training.
Rising Profits, Shifting Business Models
AI has introduced a new dynamic to the tech industry, where companies are both embracing disruptive models and struggling to sustain profitability. It is estimated that AI startups like OpenAI and Anthropic are scaling rapidly, with some reportedly reaching $30 million in revenue within 20 months. These AI startups are outperforming past SaaS companies in terms of revenue growth, driven by the fast adoption of generative AI across industries.
However, this profitability comes at a cost. Major players like OpenAI are burning through billions of dollars annually to maintain AI model development and operational costs. The capital intensity of AI investments has made it increasingly challenging for smaller companies to keep pace, while larger firms with substantial capital reserves, like Nvidia and Microsoft, have gained a competitive edge by absorbing these costs and driving industry growth.
Capital-Heavy AI Investments and Investor Realities
AI’s rise has created a paradox: while investor excitement is at an all-time high, the costs of deploying and scaling AI technology are substantial. Goldman Sachs highlights that the current wave of AI-driven growth is not a bubble; instead, the capital requirements to train and maintain AI models have created a new era of "capital-heavy" tech. Unlike the lean SaaS companies of the past, today’s AI firms need significant upfront investment in computing infrastructure, which poses risks to long-term profitability if revenue growth does not keep up with these high expenses.
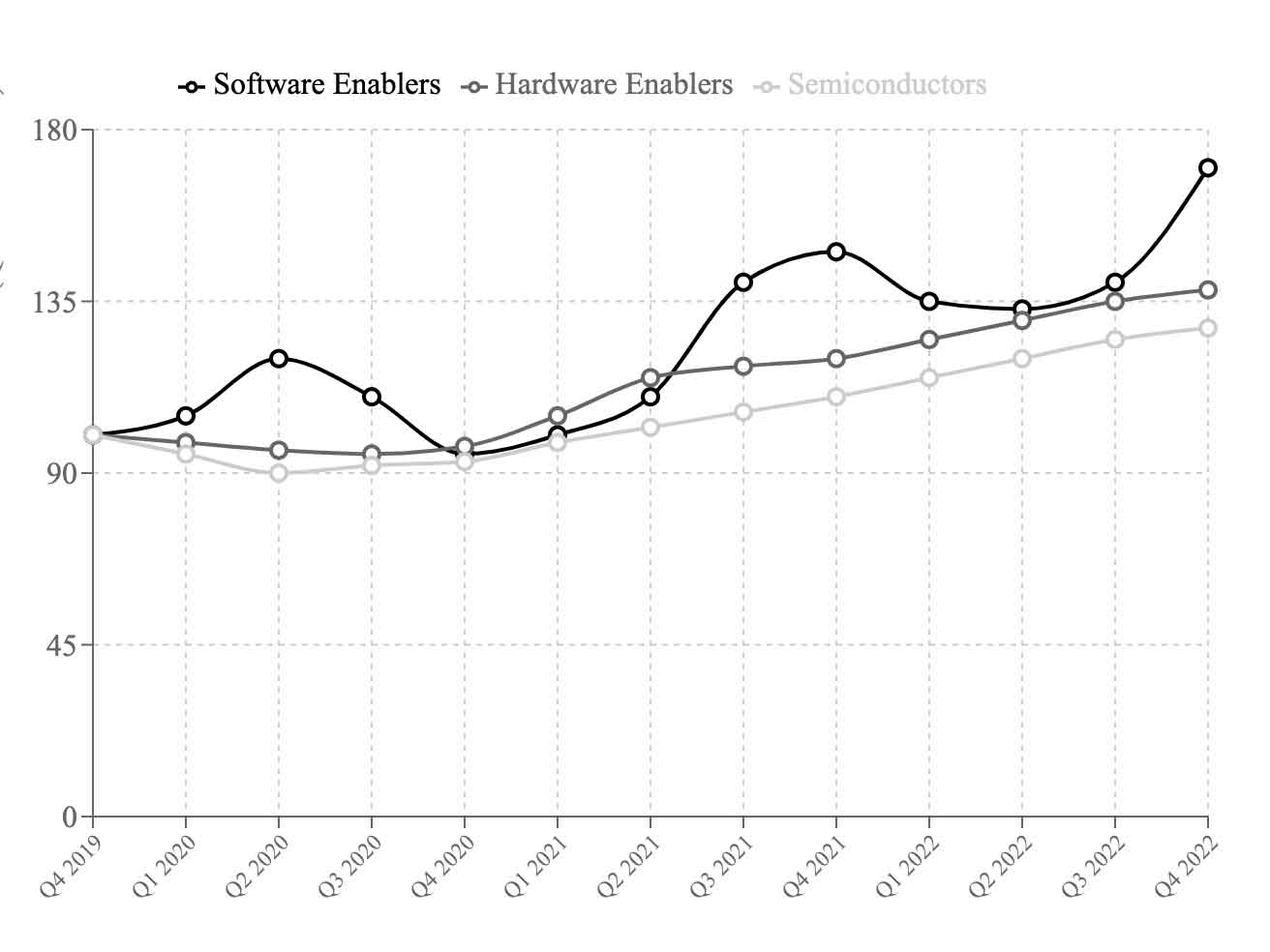
Startups, for instance, are forced to build monetization strategies early in their lifecycle, unlike the more gradual revenue growth that was typical of SaaS companies. AI businesses face a shorter runway to achieve profitability due to these large costs, and investors are closely watching to ensure that revenue aligns with their high expectations.
Investor Excitement vs. Profitability Cycles
Although investor enthusiasm for AI is high, some caution remains. As Bain's 2024 Technology Report outlines, the costs associated with AI are steep, and many businesses struggle to generate immediate value from AI deployments without operational changes. The financial reality is that many companies are still in the experimental phase of AI adoption, which limits profitability. Even large corporations are finding that AI requires significant restructuring of business models and operations to realize the full potential of these investments.
In summary, while AI’s transformative potential is reshaping the tech industry’s profitability landscape, the financial burden of AI infrastructure, training, and deployment requires both startups and incumbents to innovate rapidly while managing escalating costs. Investors, meanwhile, must balance their excitement for the technology with a clear-eyed understanding of the financial risks involved in this new, capital-heavy era of AI.
Innovation Wars: Who’s Leading the AI Race?
The AI race in 2024 is defined not only by the unprecedented growth in AI adoption but by the surge in innovation, patent filings, and intellectual property battles that are shaping the landscape. The competition between Big Tech and startups is heating up as both sides vie for dominance in this new era of technological disruption.
The Surge in AI Patents and Intellectual Property Wars
AI has sparked a wave of innovation across sectors, and this is reflected in the rapid rise of AI-related patent filings. According to the Goldman Sachs report, in 2022 alone, over 60,000 AI patents were filed, up from just 8,000 four years earlier. This explosion in intellectual property highlights the fierce competition to claim ownership over critical AI technologies. Tech giants like Nvidia, Microsoft, and Alphabet have been at the forefront of this patent surge, leveraging their extensive R&D resources to secure key AI patents that could solidify their positions at the top of the AI hierarchy.
However, this rise in patent filings has also led to legal battles over intellectual property rights. As AI becomes a key driver of innovation, companies are increasingly engaging in patent wars to protect their competitive advantages. These conflicts could reshape the AI landscape, determining which companies will lead the next wave of AI innovation.
Startups vs. Big Tech: Where Innovation is Happening and Why it Matters
While Big Tech dominates the AI race in terms of resources and patent filings, innovation is not limited to large corporations. Startups are playing a crucial role in driving AI forward, particularly in niche areas that require specialized knowledge and agility. Startups like Anthropic and Mistral have developed innovative approaches to AI that challenge the dominance of incumbents. These smaller players often focus on cutting-edge applications like generative AI, autonomous systems, and AI ethics, areas where innovation is essential and Big Tech's scale can sometimes be a hindrance.
One key advantage startups have is their ability to move quickly and experiment with new ideas without being tied to legacy systems. This allows them to develop disruptive technologies that can capture market share and potentially outpace larger, slower-moving competitors. For example, the generative AI space has seen startups take the lead in creating new AI applications for content creation, language processing, and other creative tasks.
However, Big Tech is not sitting idly by. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are increasingly acquiring or investing in AI startups to stay ahead of the curve. This strategy allows them to harness the innovative power of startups while maintaining their dominant positions in the AI market.
The Brewing Rivalry: Can Disruptors Outpace the Incumbents?
The rivalry between startups and Big Tech in the AI race is intensifying. While Big Tech has the advantage of vast financial resources and established market positions, startups are proving to be formidable challengers. The rapid rise of AI-focused startups, many of which have achieved significant revenue milestones in a fraction of the time it took previous tech companies, suggests that disruptors are capable of outpacing incumbents in certain areas.
However, the challenge for startups lies in scaling their innovations. As the Bain 2024 Technology Report highlights, Big Tech’s dominance is not solely due to innovation but also to their ability to scale technologies across global markets. Startups may struggle to compete with the scale and reach of companies like Microsoft and Google, which can deploy AI solutions across vast infrastructure networks and leverage their customer bases.
Yet, the brewing rivalry between startups and Big Tech is far from settled. As AI continues to evolve, new opportunities will emerge for disruptors to carve out their own spaces in the market. Whether through breakthrough innovations, partnerships, or acquisitions, the AI race is set to be one of the defining battles in the tech industry over the coming years.
In conclusion, while Big Tech currently leads the AI race, the innovation wars are far from over. Startups are pushing the boundaries of AI technology, and their ability to outpace incumbents will depend on how well they can scale their innovations and navigate the challenges of a rapidly changing market.
The Risk of AI Monopolies
As AI transforms the global economy, there is growing concern about the concentration of power among a small number of tech titans. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and Nvidia have come to dominate the AI landscape, using their immense financial resources and technological infrastructure to drive AI innovation and shape the future of this industry. However, this centralization raises significant risks of monopolization, stifling competition and innovation, and creating a market where only the largest players can thrive.
Market Concentration and the Risk of Dominance by Tech Titans
The dominance of Big Tech in AI is not accidental. These companies have invested heavily in AI infrastructure, such as data centers and cloud computing, which are critical for training and deploying AI models. Nvidia, for example, has become the go-to provider for the GPUs that power AI workloads, and Microsoft has embedded AI into its cloud platform Azure. This control over key technologies gives these companies an almost unassailable lead, making it difficult for startups and smaller competitors to compete on equal footing.
According to a Bain & Company report, the top five tech companies now account for over 60% of the market capitalization in the tech sector. This concentration of power not only limits competition but also gives these companies the ability to dictate the direction of AI development. Startups, which have historically been drivers of innovation, are increasingly reliant on these large platforms for access to essential technologies and markets.
Why Diversification Within and Beyond AI is Crucial for Survival
In this environment, diversification becomes essential for companies looking to survive and thrive. The AI landscape is evolving rapidly, and businesses that fail to diversify beyond their initial AI applications risk being left behind. While AI is currently a driving force across industries like healthcare, marketing, and finance, companies need to expand their focus to other emerging technologies and business models to avoid over-reliance on AI.
For startups, this means leveraging AI to create value in niche markets where they can compete without directly challenging the tech giants. For larger companies, diversification involves exploring new AI applications while simultaneously investing in non-AI innovations. A diversified portfolio not only mitigates the risk of being outcompeted in a monopolized market but also allows companies to capture value from adjacent technologies like quantum computing, biotechnology, and advanced robotics.
Regulatory Threats: How Governments May React to AI Monopolization
The concentration of AI power has not gone unnoticed by regulators. Governments around the world are increasingly concerned about the monopolistic tendencies of Big Tech and the potential for these companies to control critical AI infrastructure and innovations. Regulatory bodies are already scrutinizing mergers and acquisitions in the tech space, and there is growing momentum for more stringent antitrust regulations aimed at breaking up monopolistic power in AI.
In the European Union, for example, the Digital Markets Act (DMA) is designed to curb the power of "gatekeepers" in the digital economy, a category that includes the leading AI companies. The United States is also ramping up efforts to regulate Big Tech, with lawmakers calling for stricter antitrust laws to prevent the formation of AI monopolies. As these regulatory efforts intensify, companies that have built their business models around monopolizing AI technologies may find themselves facing significant challenges.
At the same time, governments are also likely to encourage diversification in AI development, promoting competition by supporting smaller players and encouraging the adoption of open-source AI technologies. This regulatory push could help level the playing field and reduce the dominance of a few tech titans, creating a more balanced and competitive AI ecosystem.
The risk of AI monopolies is one of the most pressing challenges facing the tech industry today. With market concentration at an all-time high, and tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Nvidia controlling key AI technologies, the need for diversification and regulatory oversight has never been more urgent. For companies, survival in this environment requires a strategy that embraces diversification—both within AI and beyond—and anticipates the regulatory changes that are likely to reshape the AI landscape in the coming years. While Big Tech’s dominance may seem insurmountable, the right mix of innovation, strategic partnerships, and regulatory intervention could open up new opportunities for disruptors and smaller players to challenge the status quo.
The Next Frontier: What Lies Beyond AI
As we move into 2024, the applications of artificial intelligence are evolving beyond traditional sectors, driving innovation in industries such as healthcare, biotechnology, finance, cybersecurity, and robotics. These emerging frontiers are expanding the boundaries of AI, unlocking unprecedented opportunities for companies willing to explore new horizons.
Emerging Industries: Healthcare, Biotechnology, and Beyond
AI’s impact on healthcare is profound. From diagnostics and personalized medicine to drug discovery, AI is transforming the healthcare landscape. Machine learning models are now capable of analyzing medical data to predict disease outcomes, helping clinicians make better-informed decisions. Biotechnology firms are leveraging AI to accelerate drug discovery processes, which has traditionally taken years, by using algorithms to sift through vast datasets of chemical compounds to identify potential new drugs.
Startups and tech giants alike are investing heavily in this space. Companies such as Tempus AI are already using AI to provide healthcare diagnostics, combining massive data processing capabilities with cutting-edge AI algorithms to improve patient outcomes. The biotech industry’s integration of AI not only enhances research capabilities but also reduces the time and costs associated with drug development, making this sector one of the most promising areas of growth beyond AI’s traditional applications.
Fintech and AI's Growing Footprint in Finance
The financial sector has long embraced AI, but recent advancements in machine learning and predictive analytics are pushing fintech companies to new heights. AI is streamlining operations, enhancing customer experiences, and improving risk management strategies. For example, AI-powered platforms are enabling real-time financial analysis, fraud detection, and credit scoring, which is revolutionizing how financial services are delivered.
AI’s ability to process massive amounts of data in real time is helping fintech firms anticipate market trends and customer needs with unprecedented accuracy. This is especially important in areas like algorithmic trading, where milliseconds can make the difference between profit and loss. The adoption of AI in finance is not only improving efficiency but also democratizing access to financial services for underserved populations by reducing the cost of delivery.
Cybersecurity and Robotics: AI’s Next Wave of Breakthrough
Cybersecurity is another field where AI is poised to make significant contributions. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, traditional security measures struggle to keep up. AI-driven cybersecurity tools are capable of identifying and responding to threats in real time, often before human operators are even aware of the breach. AI’s predictive capabilities allow systems to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and patch them before they are exploited, making it an indispensable tool in the fight against cybercrime.
Moreover, the integration of AI in robotics is leading to breakthroughs in autonomous systems and industrial automation. AI-powered robots are already being used in manufacturing to perform complex tasks with a high degree of precision, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. In logistics, autonomous drones and vehicles are being deployed for delivery and inventory management, further demonstrating AI’s potential to revolutionize industries beyond its initial scope.
AI’s applications are expanding rapidly, with healthcare, biotechnology, fintech, cybersecurity, and robotics representing the next frontier. These industries are poised to benefit significantly from AI’s capabilities, enabling companies to unlock new value and innovation. As AI continues to mature, the focus will shift toward integrating these technologies into more sectors, setting the stage for the next wave of breakthroughs that will reshape industries and redefine the global economy.
Survival Strategies for Tech Leaders and Startups
As AI continues to transform industries at an unprecedented pace, both tech leaders and startups face unique challenges in navigating this highly competitive environment. To succeed in 2024 and beyond, companies must adopt survival strategies that emphasize innovation, diversification, and robust risk management.
Doubling Down on Innovation and Talent
Innovation remains a key driver for growth and survival in the AI-dominated market. Leading tech companies and ambitious startups alike are investing heavily in research and development (R&D) to stay ahead of the curve. The top five tech companies(Microsoft, Apple, Alphabet, Meta, and Amazon) spent over $223 billion on R&D in 2023, outpacing even the entire US venture capital spending. This investment is critical in driving breakthroughs in AI, machine learning, and other emerging technologies.
For startups, focusing on attracting and retaining top talent is equally vital. According to the Financial Times article, AI startups are scaling rapidly and reaching significant revenue milestones faster than previous tech waves, with some achieving $30 million in annualized revenue in just 30 months. The ability to recruit individuals with deep expertise in AI, machine learning, and data science is essential for driving innovation. Moreover, creating a culture that fosters creativity and rapid experimentation is key to maintaining a competitive edge in this fast-moving market.
Strategic Diversification: What’s Worth Exploring
In a market where AI monopolies pose a significant risk, diversification is a critical survival strategy for both tech giants and startups. Tech companies must explore opportunities beyond their core AI products and services to mitigate risks associated with market concentration and economic downturns. Bain & Company’s report highlights how strategic diversification can not only drive growth but also provide a safety net during times of market volatility.
For startups, the challenge lies in finding a balance between focusing on their core AI offerings and exploring adjacent markets. By expanding into industries such as healthcare, biotechnology, and fintech, AI startups can unlock new revenue streams and reduce their dependence on a single product or service. Additionally, investing in AI infrastructure and platforms that support a broader range of applications, from cybersecurity to robotics, can help companies capture value in sectors beyond traditional AI markets.
The Rising Importance of Risk Management in an AI-Dominated Market
With AI investments soaring and competition intensifying, effective risk management has become more important than ever. One key challenge is managing the capital-intensive nature of AI businesses. Unlike earlier waves of tech innovation, AI requires significant upfront investments in computing power, data infrastructure, and talent. This has created new pressures on both startups and established players to monetize their AI offerings quickly and efficiently.
Tech companies must adopt a more balanced approach to growth and profitability. Goldman Sachs emphasizes the importance of diversifying investments to reduce exposure to high-risk AI ventures and to seek out opportunities in smaller tech companies and traditional industries. Startups, in particular, need to carefully manage their burn rates, ensuring that their capital-intensive AI models do not drain resources before profitability is achieved.
Moreover, the regulatory environment is tightening as governments become more concerned about the monopolistic power of tech giants in the AI space. Companies must proactively address regulatory risks by engaging with policymakers and ensuring compliance with evolving AI governance frameworks. Failing to do so could lead to costly legal battles or restrictions that hinder growth.
As AI reshapes the global economy, both tech leaders and startups must adopt a multifaceted approach to survival. By doubling down on innovation and talent, strategically diversifying their portfolios, and implementing strong risk management practices, companies can position themselves to thrive in the AI-driven future. While the path ahead is fraught with challenges, those who can navigate this complex landscape will be well-equipped to lead the next wave of technological transformation.
Beyond the AI Hype—Sustaining Growth in 2024 and Beyond
The AI boom of 2024 is far more than a fleeting technological trend; it represents a seismic shift in the global business landscape. As industries continue to integrate AI into their operations, the question is not whether AI will endure but how companies can build sustainable futures in an AI-first world. The combination of unprecedented innovation, transformative business models, and shifting market dynamics suggests that the effects of AI will reverberate well into the next decade and beyond.
Why the AI Boom Is More Than Just a Passing Trend
AI's impact is not limited to technology sectors—it spans industries as diverse as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. The rapid adoption of AI-driven tools for diagnostics, automation, and decision-making reflects its central role in increasing operational efficiency and enhancing productivity across the board. Bain & Company highlights that AI, when integrated strategically, can drive as much as 20% gains in EBITDA for companies that fully rework their processes to leverage AI. This is not merely a technology hype cycle; AI is a fundamental enabler of future business growth.
The critical difference between AI and previous technological innovations lies in its capacity to learn, evolve, and optimize autonomously. This self-improving nature of AI ensures that its relevance and value will continue to grow as models become more sophisticated. Moreover, the competitive pressure to innovate will push companies—both tech giants and startups—to continually develop more advanced AI applications, ensuring that the momentum behind AI's expansion is sustained.
How Companies Can Build Sustainable Futures in an AI-First World
Building a sustainable future in an AI-first world requires a multi-pronged approach. First, companies need to balance short-term returns with long-term innovation. As Goldman Sachs notes, the current high levels of investment in AI are grounded in strong financial fundamentals, driven by earnings growth and operational efficiency gains, especially in sectors like cloud computing. Companies must continue to invest in AI infrastructure, such as data centers and high-performance computing resources, while also fostering a culture of continuous innovation.
Additionally, talent remains a critical factor in sustaining AI growth. As AI evolves, the demand for highly skilled workers in machine learning, data science, and AI ethics will only intensify. Startups and large corporations alike must invest in recruiting and developing this talent, creating a workforce capable of handling the complexity and breadth of AI applications.
Strategic diversification is another key to long-term success. Companies should explore opportunities both within and beyond AI to mitigate risks and capture value from adjacent markets. For instance, startups leveraging AI in niche markets, such as biotechnology or fintech, are positioned to unlock new revenue streams and secure a competitive edge. Meanwhile, tech giants must diversify their AI offerings to address multiple industries, ensuring that they are not overly reliant on any single market.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for the Tech Giants and the Disruptors?
The future of AI is bright, but it is not without challenges. While tech giants like Microsoft, Nvidia, and Google currently dominate the AI landscape, new competitors are likely to emerge. The next wave of innovation will likely come from smaller, agile startups that find unique applications for AI and leverage disruptive technologies like quantum computing, blockchain, and advanced robotics.
At the same time, regulatory scrutiny will play an increasingly important role in shaping the AI landscape. Governments are likely to introduce new frameworks to address ethical concerns, data privacy, and the potential monopolization of AI technologies. This will create both challenges and opportunities for companies operating in the AI space.
For disruptors, the challenge will be scaling their innovations while navigating an environment dominated by powerful incumbents. But history has shown that disruptive startups, with the right combination of innovation, talent, and strategic partnerships, can outpace even the largest tech giants.
In conclusion, the AI boom is far from a temporary surge—it's the dawn of a new technological era. Companies that embrace innovation, invest in talent, and strategically diversify their portfolios will not only survive but thrive in this AI-first world. The race is far from over, and the future promises a dynamic landscape where tech giants and disruptors alike can play pivotal roles in shaping the next chapter of AI-driven growth.
References
- William & Mary Online | The Future of Finance: AI, Machine Learning & Predictive Analytics
- Weka.io | 2024 Global Trends in AI
- IMF Blog | AI Will Transform the Global Economy—Let's Make Sure It Benefits Humanity
- Financial Times | The disruptive power of AI: Will the tech giants dominate the future?
- CNBC | The gap between AI expectations and outcomes in the workplace are wide
- Goldman Sachs | AI Stocks Aren't in a Bubble
- CNBC | The AI craze is getting funded by tech giants, distorting traditional VCs
- Bain Insights | Technology Report
- MIT Technology Review | Generative AI: Differentiating Disruptors From the Disrupted
Please Note: This content was created with AI assistance. While we strive for accuracy, the information provided may not always be current or complete. We periodically update our articles, but recent developments may not be reflected immediately. This material is intended for general informational purposes and should not be considered as professional advice. We do not assume liability for any inaccuracies or omissions. For critical matters, please consult authoritative sources or relevant experts. We appreciate your understanding.
